Sitemap
A list of all the posts and pages found on the site. For you robots out there is an XML version available for digesting as well.
Pages
Posts
portfolio
Disease Prediction Model
An Analysis of Lassa Fever Outbreaks in Nigeria using Machine Learning Models and Shapley Values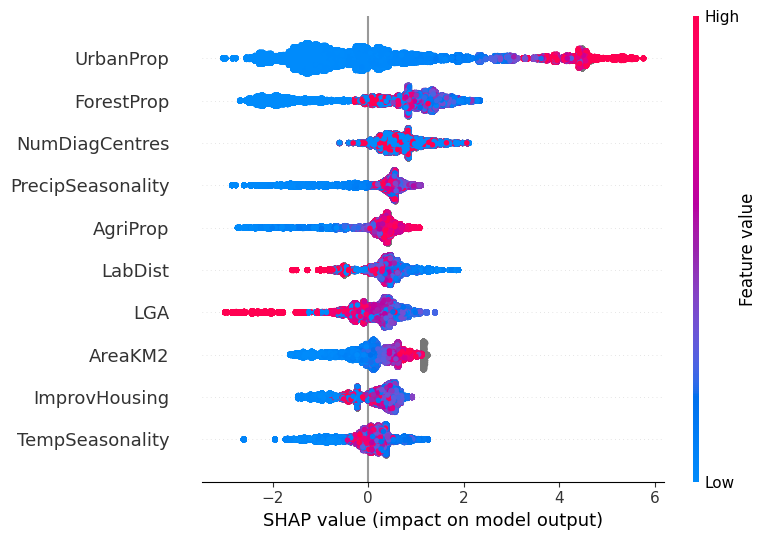
Infectious Disease Dashboard
A Real-Time Data-Driven Infectious Disease Dashboard to Monitor 2022-2023 Global Mpox Outbreak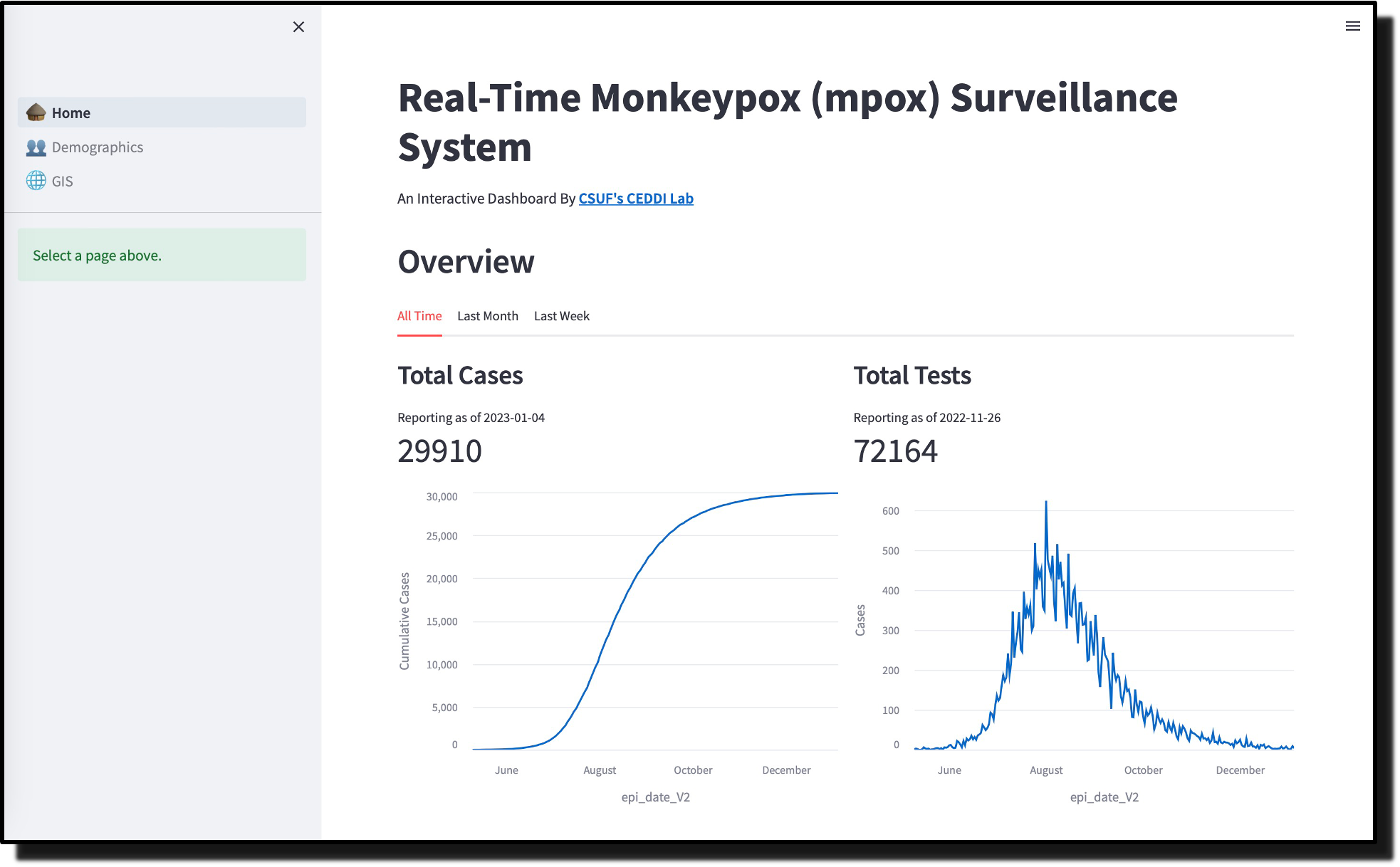
publications
Real-Time Hybrid Dashboard and App for Mpox Outbreak Surveillance
Published in IEEE Global Humanitarian Technology Conference (GHTC), 2023
With the continuous rise in the global threat of infectious diseases, surveillance systems have become powerful tools for monitoring the development and transmission patterns of fast-changing disease outbreaks, by public health officers. These surveillance systems typically track relevant epidemiological data such as number of cases, fatality rates, hot spots, and in most cases, evaluate the impact of public health intervention strategies in these locations. Data from these surveillance apps can also be used for efficient emergency response preparatory logistics, as well as early containment. In this paper, we presents a modular, open-source, GIS-enabled, web-based dashboard and mobile app that are capable of visualizing and identifying epidemiological patterns for any infectious disease of interest, in real time. These visualizations can be in the form of GIS maps, charts, and other metrics to track certain indicators. Python and Streamlit library are used to manage the frontend of the application. Data from the 2022 Mpox outbreak in the United States were used to evaluate the application. Nongovernmental organizations or other community-based groups can leverage on, and adapt this dashboard to monitor the spread of any quick-onset disease outbreak in their regions.
Recommended citation: D. Quezada, S. Akwafuo, and A. Wattamwar, "Real-Time Hybrid Dashboard and App for Mpox Outbreak Surveillance," presented at the 2023 IEEE Global Humanitarian Technology Conference (GHTC), Radnor, PA, USA, 2023, pp. 433-439, doi: [10.1109/GHTC56179.2023.10355026](https://doi.org/10.1109/GHTC56179.2023.10355026). http://danielquezada.com/files/mpox.pdf
Harnessing Machine Learning for Predictive Analytics: A Case Study of Lassa Fever Outbreaks in Nigeria
Published in IEEE International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies, 2024
In this project, I worked on building machine learning models to predict Lassa Fever outbreaks across Nigeria. Using epidemiological, socio-economic, and eco-climatic data, we were able to uncover patterns driving Lassa transmissions.
Recommended citation: D. Quezada, S. Akwafuo, and S. Halyal, "Harnessing Machine Learning for Predictive Analytics: A Case Study of Lassa Fever Outbreaks in Nigeria" 2024 10th International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies (CoDIT), Vallette, Malta, 2024, pp. 377-382, doi: 10.1109/CoDIT62066.2024.10708095. http://danielquezada.com/files/lassa.pdf
